In April 2021, Pangyo was designated as a demonstration zone for autonomous vehicle technologies and related services. To beef up the development of self-driving technology and mobility services such as car-sharing and self-driving taxi-hailing, South Korea's transport ministry designated six cities including Seoul and the central city of Sejong as demonstration zones in 2020. Pangyo was the seventh zone.
Prior to the ministry's decision, the town district in Seongnam already established a built-in road infrastructure for self-driving cars. It has a control tower and an internet of things (IoT) service network that enables road structures such as traffic lights to communicate with other structures and vehicles using vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication technology.
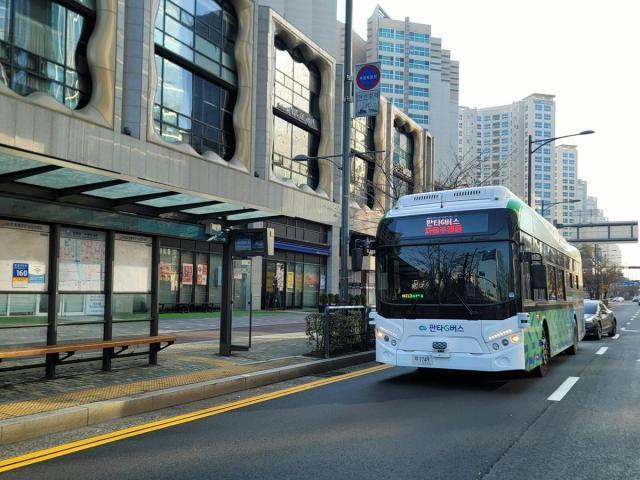
The Gyeonggi provincial government said that two PanTa-G Buses carried a total of 10,002 passengers over the four-month period, covering about 11,714 kilometers. The buses operate 24 times a day at 30-minute intervals, running from 7:30 a.m. to 7 p.m. on weekdays. The vehicle has a total of 14 seats including two spots for the transportation vulnerable.
South Korea's capital city also unveiled its plan to adopt more than 300 self-driving vehicles and related services by 2026. In February 2022, Seoul commercialized an autonomous vehicle-hailing service in its western district by deploying four autonomous vehicles. The city is also running self-driving buses near Cheonggyecheon, a stream that flows through the heart of the capital city.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.